Announcements
Jan 5, 2026
Fermi Cycle 19 Proposal workshop, including TOOs
The Fermi Science Support Center (FSSC) is hosting a virtual proposal workshop on 14 January 2026 from 2:00-3:30PM EST. Full details, including a link to the registration form, can be found on the Workshop Page. The workshop will include details of the updated Target of Opportunity (TOO) program. Please register by 10AM EST on Jan 14 so that we can send you the details to join the virtual meeting.
Dec 18, 2025
Fermitools 2.5.0 Released
An updated version (2.5.0) of the Fermitools is now available. A large number of changes have been made focusing on resolving issues with dependencies, internal tool testing and validation, and resolving outstanding issues. These changes include packaging a set of external dependencies with the tools for improved build and installation performance, a range of bug fixes and enhancements to backend code, and a complete overhaul of the FSSC build system.
+ Release Notes
Dec 10, 2025
Refreshed Website
A refreshed version of the Fermi website (fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov) went live yesterday. The update enhances navigation, introduces new content, retires outdated pages, and brings the site into alignment with current U.S. government and HEASARC design standards.
If you notice any issues, missing material, or have suggestions for further improvements, please share your feedback using the Google form below. We plan to release another update in February 2026 informed by the community response.
+ https://forms.gle/4AQaPBUoRwzApNcz8
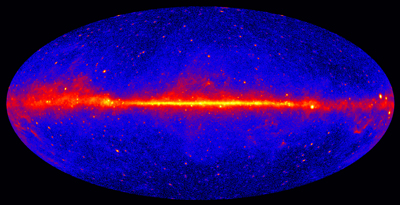
Events
Fermi Proposal deadline January 29, 2026. Fermi Cycle 19 →

Fermi Research
Highlights of Fermi discoveries and and latest breakthroughs. Explore More →

New Fermi Users
A starting point for first-time Fermi users. Explore More →

Science Community
Access data, tools, and resources for scientific research with Fermi.


